The innovative results of a study on the effects of a synthetic oil on brain metabolism in Huntington disease, performed by researchers in the Institut du Cerveau – ICM were just published in the journal Neurology.
The results of this study, carried out on 10 patients treated for a month at an early stage of the disease, hold promise for a new treatment for this neurodegenerative disease. This medicinal oil seems to correct brain energy metabolism, which is abnormal in patients and contributes to the progression of their symptoms. This project represents an important advance for the discovery of new treatments, and a license for its use has been signed with the company ULTRAGENYX for the development of therapeutic agents.
A hereditary neurodegenerative disorder, Huntington disease is linked to an autosomal dominantly transmitted genetic abnormality. The signs of the disease usually appear between age 30 and 50 years with the emergence of progressive motor, behavioural and psychiatric disorders, which lead to dependency and affect the entire family.
The only treatments available at present are symptomatic treatments that improve the psychiatric and certain motor disorders of the disease. There is, however, no treatment that can change the course of the disease, although the genetic anomaly has been known since 1993. Dr. Fanny Mochel, in collaboration with Pr. Alexandra Durr, has worked for several years in the team of Pr. Alexis Brice at the Institut du Cerveau – ICM to validate a metabolic therapeutic hypothesis in Huntington disease.
The researchers had previously observed that non-neurological disorders could be detected during the presymptomatic stage of Huntington disease – in which carriers of the genetic abnormality do not yet express symptoms. In question is an alteration of energy metabolism manifested by loss of weight, despite a high calorie diet, and a decrease in compounds in the blood indicative of an increased need for certain energy intermediates. Dr. Fanny Mochel previously established that the synthetic oil triheptanoin could furnish the energy intermediates in question. It was, therefore, hypothesized that triheptanoin might improve, even correct, the energy deficit in both the brain and the periphery in Huntington disease.
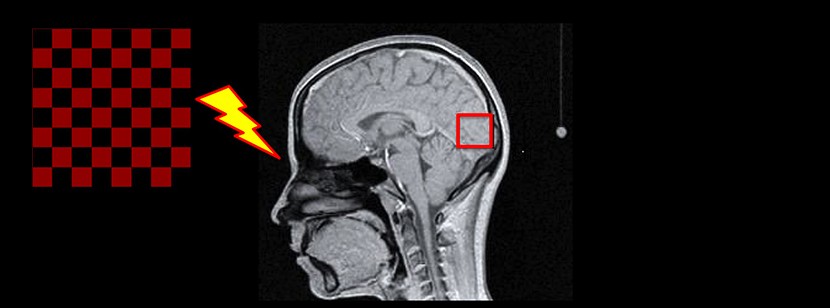
Before launching a therapeutic trial to determine the long term clinical benefits of this treatment, the researchers needed to demonstrate that triheptanoin was indeed capable of improving energy metabolism in the brains of patients with Huntington disease. To this end, they analysed, after a month of treatment, the effects of the synthetic oil tripeptanoin – a saturated fatty acid with 7 carbon atoms – on 10 patients with the genetic anomaly at the beginning of the disease and 13 control subjects.
With a functional imaging technique using magnetic resonance spectroscopy developed by the researchers of the Institut du Cerveau – ICM in collaboration with the CENIR – Centre de Neuroimagerie de Recherche (Neuroimaging Research Centre) of the Institut du Cerveau – ICM – and an American team in Minneapolis – The Center for Magnetic Resonance Research – the researchers were able to measure the energy produced in the visual cortex of patients – a region known for its elevated energy metabolism – during a visual stimulus, before and after a month’s treatment with triheptanoin at a dose of 6 soup spoons a day taken at mealtimes.
The results obtained in this study are very encouraging, since they show that, after only 1 month of treatment, the abnormal brain energy profile of patients with Huntington disease was corrected, approaching the energy profile of the control subjects. Furthermore, a decrease in the motor dysfunctions of the disease, measured with the use of an international scale, was observed, but must be interpreted with caution given the absence of a placebo group in the study.
The results obtained offer great hopes for Huntington disease patients and establish the proof of concept that this oil is a possible candidate molecule for future treatments. It is now necessary to evaluate the benefit of this treatment on clinical and imaging markers in a larger number of patients with Huntington disease. With this aim, a licence for use has been obtained from ULTRAGENYX, the company that commercializes triheptanoin.