Objective: To develop a novel approach to generate individual maps of white matter (WM) innate immune cell activation using 18F-DPA-714 translocator protein (TSPO) positron emission tomography (PET), and to explore the relationship between these maps and individual trajectories of disability worsening in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS).
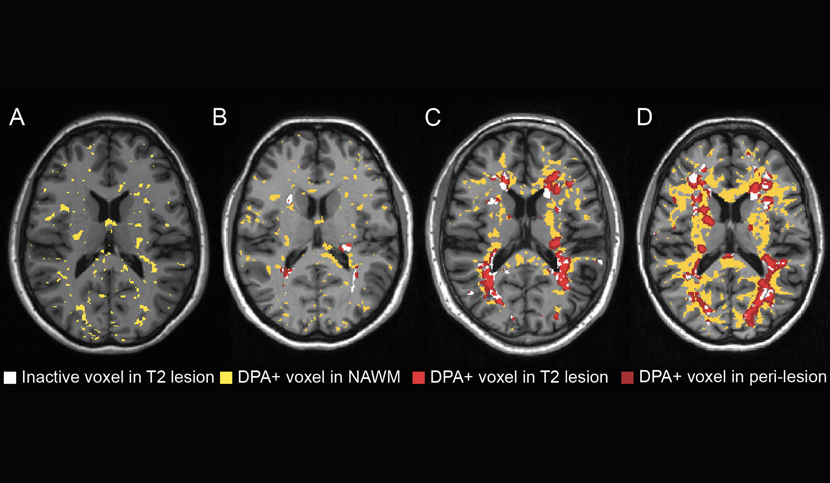
Methods: Patients with MS (n = 37), whose trajectories of disability worsening over the 2 years preceding study entry were calculated, and healthy controls (n = 19) underwent magnetic resonance magnetic and 18F-DPA-714 PET. A threshold of significant activation of 18F-DPA-714 binding was calculated with a voxel-wise randomized permutation-based comparison between patients and controls, and used to classify each WM voxel in patients as characterized by a significant activation of innate immune cells (DPA+) or not. Individual maps of innate immune cell activation in the WM were employed to calculate the extent of activation in WM regions-of-interests and to classify each WM lesion as “DPA-active”, “DPA-inactive” or “unclassified”.
Results: Compared with the WM of healthy controls, patients with MS had a significantly higher percentage of DPA+ voxels in the normal-appearing WM, (NAWM in patients=24.9±9.7%; WM in controls=14.0±7.8%, p<0.001). In patients with MS, the percentage of DPA+ voxels showed a significant increase from NAWM, to perilesional areas, T2 hyperintense lesions and T1 hypointense lesions (38.1±13.5%, 45.0±17.9%, and 51.9±22.9%, respectively, p<0.001). Among the 1379 T2 lesions identified, 512 were defined as DPA-active and 258 as DPA-inactive. A higher number of lesions classified as DPA-active (OR=1.13, P = 0.009), a higher percentage of DPA+ voxels in the NAWM (OR=1.16, P = 0.009) and in T1-spin-echo lesions (OR=1.06, P = 0.036), were significantly associated with a retrospective more severe clinical trajectory in patients with MS.
Conclusion: A more severe trajectory of disability worsening in MS is associated with an innate immune cells activation inside and around WM lesions. 18F-DPA-714 PET may provide a promising biomarker to identify patients at risk of severe clinical trajectory.
Source
Individual mapping of innate immune cell activation is a candidate marker of patient-specific trajectories of disability worsening in Multiple Sclerosis. Bodini B, et al. J Nucl Med 2020.